This topic gives you step-by-step instructions to make your PowerPoint presentations accessible to people with disabilities.

PowerPoint presentations tend to be highly visual, and people who are blind or have low vision can understand them more easily if you create your slides with accessibility in mind.
Windows: Best practices for making PowerPoint presentations accessible
The following table includes key best practices for creating PowerPoint presentations that are accessible to people with disabilities.
| What to fix | How to find it | Why fix it | How to fix it |
|---|---|---|---|
| Include alternative text with all visuals. Visual content includes pictures, SmartArt graphics, shapes, groups, charts, embedded objects, ink, and videos. | To find missing alternative text, use the Accessibility Checker. | Alternative text helps people who can’t see the screen to understand what’s important in images and other visuals. Avoid using text in images as the sole method of conveying important information. If you must use an image with text in it, repeat that text in the presentation. In the alternative text, briefly describe the image and mention the existence of the text and its intent. | Add alt text to visuals in Microsoft 365 |
| Make sure slide contents can be read in the order that you intend. | Use the Accessibility Checker to find slides that have possible problems with reading order. | When someone who can see reads a slide, they usually read things, such as text or a picture, in the order the elements appear on the slide. In contrast, a screen reader reads the elements of a slide in the order they were added to the slide, which might be very different from the order in which things appear. To make sure everyone reads the contents in the order you intend, it's important to check the reading order. | |
| When creating a new slide, use the built-in slide designs. | PowerPoint contains built-in slide layouts that you can apply to any slide. When you use them with a new slide, these layouts automatically make sure that the reading order works for everyone. | ||
| Add meaningful hyperlink text and ScreenTips. | To determine whether hyperlink text makes sense as standalone information and whether it gives readers accurate information about the destination target, visually scan the slides in your presentation. | People who use screen readers sometimes scan a list of links. Links should convey clear and accurate information about the destination. For example, instead of linking to the text Click here, include the full title of the destination page. You can even use the URL of the page if it's short and descriptive, for example, www.microsoft.com. Tip: You can also add ScreenTips that appear when your cursor hovers over text or images that include a hyperlink. | |
| Ensure that color is not the only means of conveying information. | Switch to the View tab and select Grayscale. Visually scan each slide in your presentation for instances of color-coding. | People who are blind, have low vision, or are colorblind might miss out on the meaning conveyed by particular colors. For example, add an underline to color-coded hyperlink text so that people who are colorblind know that the text is linked even if they can’t see the color. For headings, consider adding bold or using a larger font. | |
| Use sufficient contrast for text and background colors. | To find insufficient color contrast, use the Accessibility Checker. You can also look for text in your spreadsheet that’s hard to read or to distinguish from the background. | Use strong contrast between text and background, so people with low vision can see and use the content. Use dark text on a white or off-white background, or reverse it and use white text on a dark background. White and black schemes also make it easier for people who are colorblind to distinguish text and shapes. | |
| Give every slide a unique title | To find slides that do not have titles, use the Accessibility Checker. | People who are blind, have low vision, or a reading disability rely on slide titles to navigate. For example, by skimming or using a screen reader, they can quickly scan through a list of slide titles and go right to the slide they want. | |
| Use a simple table structure, and specify column header information. | To ensure that tables don't contain split cells, merged cells, or nested tables, use the Accessibility Checker. | Screen readers keep track of their location in a table by counting table cells. If a table is nested within another table or if a cell is merged or split, the screen reader loses count and can’t provide helpful information about the table after that point. Screen readers also use header information to identify rows and columns. | |
| Use a larger font size (18pt or larger), sans serif fonts, and sufficient white space. | To find potential issues related to fonts or white space, review your slides for areas that look crowded or illegible. | People who have dyslexia describe seeing text “swim together” on a page (the compressing of one line of text into the line below). They often see text merge or distort. For people who have dyslexia or have low vision, reduce the reading load. For example, they may benefit from familiar sans serif fonts, such as Arial or Calibri. Avoid using all capital letters and excessive italics or underlines. Include ample white space between sentences and paragraphs. | |
| Make videos accessible to visually impaired and hearing-impaired users. | Subtitles typically contain a transcription (or translation) of the dialogue. Closed captions typically also describe audio cues such as music or sound effects that occur off-screen. Video description means audio-narrated descriptions of a video's key visual elements. These descriptions are inserted into natural pauses in the program's dialogue. Video description makes video more accessible to individuals who are blind or visually impaired. | Use captions, subtitles, and alternative audio tracks in videos |
Add alt text to visuals in Microsoft 365
The following procedures describe how to add alt text to visuals in your PowerPoint presentations in Microsoft 365:
Note: For audio and video content, in addition to alt text, include closed captioning for people who are deaf or have limited hearing.
Tip: To write a good alt text, make sure to convey the content and the purpose of the image in a concise and unambiguous manner. The alt text shouldn’t be longer than a short sentence or two—most of the time a few thoughtfully selected words will do. Do not repeat the surrounding textual content as alt text or use phrases referring to images, such as, "a graphic of" or "an image of."
Add alt text to images
PowerPoint does not automatically generate alt texts for drawn images, such as diagrams or icons. If you want to add an image that is an icon, screenshot, or other image that is not a photograph, you need to add the alt texts manually.
-
Do one of the following:
-
Right-click an image and select Edit Alt Text.
-
Select an image. Select Format > Alt Text.
The Alt Text pane opens on the right side of the slide.
-
-
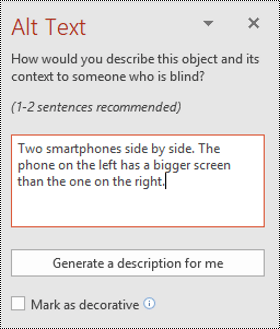
Type 1-2 sentences to describe the image and its context to someone who cannot see it.
Tip: To spell check and correct a word you typed, just right-click the word and select from the suggested alternatives.
Tip: You can also select Generate a description for me to have Microsoft's cloud-powered intelligent services create a description for you. This takes a moment, after which you see the result in the text entry field. Remember to delete any comments PowerPoint added there, for example, "Description generated with high confidence."
Add alt text to shapes or SmartArt graphics
-
Do one of the following:
-
Right-click a shape or SmartArt graphic and select Edit Alt Text.
Tip: You have to right-click somewhere inside the frame that surrounds the entire shape or SmartArt graphic, not inside one of its parts.
-
Select a shape or a SmartArt graphic. Select Format > Alt Text.
The Alt Text pane opens on the right side of the slide.
-
-
Type 1-2 sentences to describe the shape or SmartArt graphic and its context to someone who cannot see it.
Tip: To spell check and correct a word you typed, just right-click the word and select from the suggested alternatives.
Add alt text to charts
-
Do one of the following:
-
Right-click a chart and select Edit Alt Text.
Tip: You have to right-click somewhere inside the frame that surrounds the entire chart, not inside one of its parts.
-
Select a chart. Select Format > Alt Text.
The Alt Text pane opens on the right side of the slide.
-
-
Type 1-2 sentences to describe the chart and its context to someone who cannot see it.
Tip: To spell check and correct a word you typed, just right-click the word and select from the suggested alternatives.
Review or edit automatically generated alt texts in photos
PowerPoint for PC in Microsoft 365 automatically generates alt texts for photos by using intelligent services in the cloud. You can review and edit the autogenerated alt texts.
-
To open the Alt Text pane, do one of the following:
-
Right-click an image, and then select Edit Alt Text.
-
Select an image. Select Format > Alt Text.
-
-
In the Alt Text pane, review the description in the text box.
-
Do one of the following:
-
To accept the suggested text, close the Alt Text pane and return to the PowerPoint slide.
-
To change the suggested alt text, type your preferred text in the box. Once you're done, close the Alt Text pane and return to the PowerPoint slide.
-
Mark visuals as decorative
If your visuals are purely decorative and add visual interest but aren't informative, you can mark them as such without needing to write any alt text. Examples of objects that should be marked as decorative are stylistic borders. People using screen readers will hear that these objects are decorative so they know they aren’t missing any important information.
-
To open the Alt Text pane, do one of the following:
-
Right-click an image, and then select Edit Alt Text.
-
Select an image. Select Format > Alt Text.
-
-
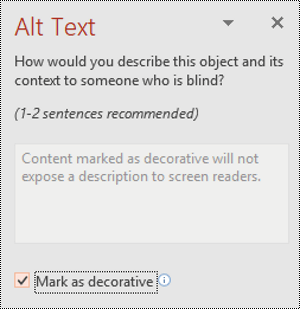
Select the Decorative check box. The text entry field becomes grayed out.
Add alt text to visuals in Office 2019
The following procedures describe how to add alt text to visuals in your PowerPoint presentations in Office 2019:
Note: For audio and video content, in addition to alt text, include closed captioning for people who are deaf or have limited hearing.
Tip: To write a good alt text, make sure to convey the content and the purpose of the image in a concise and unambiguous manner. The alt text shouldn’t be longer than a short sentence or two—most of the time a few thoughtfully selected words will do. Do not repeat the surrounding textual content as alt text or use phrases referring to images, such as, "a graphic of" or "an image of."
Add alt text to images
PowerPoint does not automatically generate alt texts for drawn images, such as diagrams or icons. If you want to add an image that is an icon, screenshot, or other image that is not a photograph, you need to add the alt texts manually.
-
Do one of the following:
-
Right-click an image and select Edit Alt Text.
-
Select an image. Select Format > Alt Text.
The Alt Text pane opens on the right side of the slide.
-
-
Type 1-2 sentences to describe the image and its context to someone who cannot see it.
Tip: To spell check and correct a word you typed, just right-click the word and select from the suggested alternatives.
Tip: You can also select Generate a description for me to have Microsoft's cloud-powered intelligent services create a description for you. This takes a moment, after which you see the result in the text entry field. Remember to delete any comments PowerPoint added there, for example, "Description generated with high confidence."
Add alt text to shapes or SmartArt graphics
-
Do one of the following:
-
Right-click an shape or SmartArt graphic and select Edit Alt Text.
Tip: You have to right-click somewhere inside the frame that surrounds the entire shape or SmartArt graphic, not inside one of its parts.
-
Select a shape or a SmartArt graphic. Select Format > Alt Text.
The Alt Text pane opens on the right side of the slide.
-
-
Type 1-2 sentences to describe the shape or SmartArt graphic and its context to someone who cannot see it.
Tip: To spell check and correct a word you typed, just right-click the word and select from the suggested alternatives.
Add alt text to charts
-
Do one of the following:
-
Right-click a chart and select Edit Alt Text.
Tip: You have to right-click somewhere inside the frame that surrounds the entire chart, not inside one of its parts.
-
Select a chart. Select Format > Alt Text.
The Alt Text pane opens on the right side of the slide.
-
-
Type 1-2 sentences to describe the chart and its context to someone who cannot see it.
Tip: To spell check and correct a word you typed, just right-click the word and select from the suggested alternatives.
Mark visuals as decorative
If your visuals are purely decorative and add visual interest but aren't informative, you can mark them as such without needing to write any alt text. Examples of objects that should be marked as decorative are stylistic borders. People using screen readers will hear that these objects are decorative so they know they aren’t missing any important information.
-
To open the Alt Text pane, do one of the following:
-
Right-click an image, and then select Edit Alt Text.
-
Select an image, Select Format > Alt Text.
-
-
Select the Decorative check box. The text entry field becomes grayed out.
Add alt text to visuals in Office 2016
The following procedures describe how to add alt text to visuals in your PowerPoint presentations in Office 2016:
Note: We recommend only putting text in the description field and leaving the title blank. This will provide the best experience with most major screen readers including Narrator. For audio and video content, in addition to the alt text, include closed captioning for people who are deaf or have limited hearing.
Review or edit automatically generated alt texts in photos
PowerPoint for PC in Microsoft 365 automatically generates alt texts for photos by using intelligent services in the cloud. You can review and edit the autogenerated alt texts.
Note: This feature is only available to Microsoft 365 subscribers who have joined the Office Insider program. If you are a Microsoft 365 subscriber, make sure you have the latest version of Office.
-
Right-click an image.
-
Select Edit Alt Text to open the Alt Text pane.
-
In the Alt Text pane, review the description in the text box.
-
Do one of the following:
-
To accept the suggested text, close the Alt Text pane and return to the PowerPoint slide.
-
To change the suggested alt text, type your preferred text in the box. Once you're done, close the Alt Text pane and return to the PowerPoint slide.
-
Add alt text to images
PowerPoint does not automatically generate alt texts for drawn images, such as diagrams or icons. If you want to add an image that is an icon or other image that is not a photograph, you need to add the alt texts manually.
-
Right-click an image and select Size and Position.
-
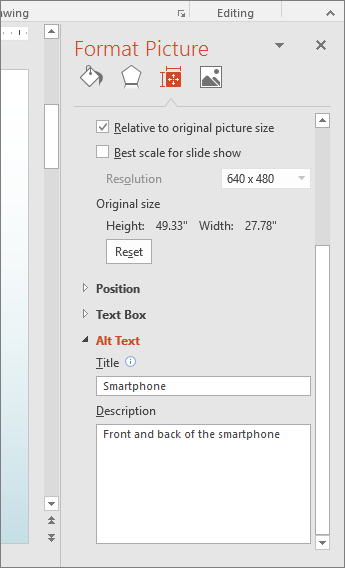
In the Format Picture pane, select Alt Text.
-
In the text box, type the alt text for the image.
Add alt text to SmartArt graphics
-
Right-click a SmartArt graphic and select Size and Position.
-
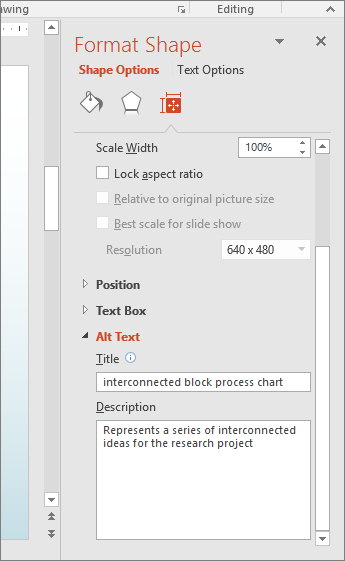
In the Format Shape pane, select Alt Text and type a description for the graphic.
Tip: Include the most important information in the first line, and be as concise as possible.
Add alt text to shapes
Add alt text to shapes, including shapes within a SmartArt graphic.
-
Right-click a shape and select Size and Position.
-
In the Format Shape pane, select Alt Text and type a description for the shape.
Tip: Include the most important information in the first line, and be as concise as possible.
Add alt text to charts
-
Right-click a chart and select Format Chart Area.
-
In the Format Chart Area pane, select Size & Properties.
-
Select Alt Text and type a description for the chart.
Tip: Include the most important information in the first line, and be as concise as possible.
Make hyperlinks, text, and tables accessible
The following procedures describe how to make the hyperlinks, text, and tables in your PowerPoint presentations accessible.
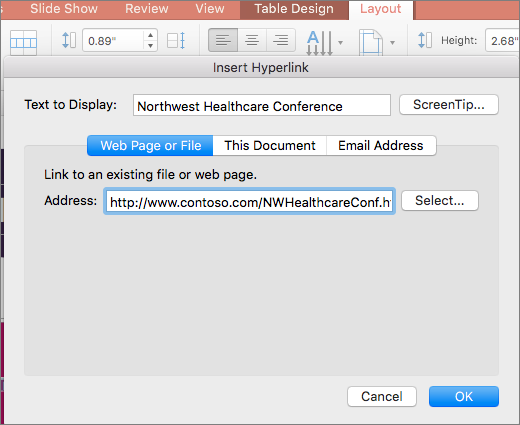
Add hyperlink text and ScreenTips
-
Select the text to which you want to add the hyperlink, and then right-click.
-
Select Link. The text you selected displays in the Text to display box. This is the hyperlink text.
-
If necessary, change the hyperlink text.
-
In the Address box, enter the description address for the hyperlink.
-
Select the ScreenTip button and, in the ScreenTip text box, type a ScreenTip.
Tip: If the title on the hyperlink's destination page gives an accurate summary of what’s on the page, use it for the hyperlink text. For example, this hyperlink text matches the title on the destination page: Templates and Themes for Office Online.
-
To apply the changes, select OK > OK.
Use an accessible slide design
Use one of the included accessible templates to make sure that your slide design, colors, contrast, and fonts are accessible for all audiences. They are also designed so that screen readers can more easily read the slide content.
-
To find an accessible template, select File > New.
-
In the Search for Online templates and themes text field, type accessible templates and press Enter.
-
In the search results, select a suitable template.
-
In the template preview window, select Create.
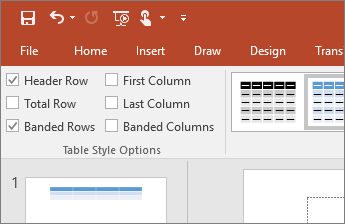
Use table headers
-
Position the cursor anywhere in a table.
-
Select the Design tab.
-
In the Table Style Options, select the Header Row check box.
-
In the table, type the column headings.
Format text for accessibility
-
Select your text.
-
Select the Home tab.
-
In the Font group, which provides options for font type, size, style, and color, select your formatting choices.
Use accessible text color
Here are some ideas to consider:
-
Use the pre-designed Office Themes to make sure that your slide design is accessible. For instructions, see Use an accessible slide design.
-
Use the Accessibility Checker to analyze the presentation and find insufficient color contrast. It checks the text in the slides against the following elements:
-
Page color
-
Cell backgrounds
-
Highlights
-
Text box fill
-
Paragraph shading
-
SmartArt fills
-
Headers and footers
-
Links
-
Make slides accessible
The following procedures describe how to make the slides in your PowerPoint presentations accessible. (See Title a slide for related information.)
Give every slide a title
-
Select Review > Check Accessibility to check your presentation for issues.
One simple step towards inclusivity is having a title on each slide, even if it isn't visible. Accessibility Checker can point out four situations where a title is warranted:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Edit Slide Title | Appears if the slide already has a title placeholder and you just need to fill it in. |
| Add Slide Title | Appears when a slide doesn’t have a title placeholder. Choosing this option adds a title placeholder even if the Slide Layout you used didn’t have one. Fill it in with the title you want to use. |
| Add Hidden Slide Title | Appears if the slide already has a title placeholder and you just need to fill it in. The placeholder is positioned off the slide so that it's invisible during Slide Shows and in printouts. |
| Set as Slide Title | Appears when the slide has no title placeholder. When you choose this command, PowerPoint automatically selects what it thinks is the most likely text box to be the title. But you can change the selection if necessary. |
Use unique slide titles
-
To restore all placeholders for the selected slide, on the Home tab, in the Slides group, select Reset.
-
On the slide, type a unique and descriptive title.
Hide a slide title
Position a title off-slide, so it will be invisible but will still be voiced by screen readers.
-
On the View tab, select Zoom and then lower the zoom percentage to about 50% so that the margins outside the slide are visible.
-
Point the mouse at the border of the Title placeholder box so that the pointer becomes a four-headed move pointer.
-
Drag the Title placeholder upward or downward and then drop it outside the slide boundary.
Set the reading order of slide contents
Use the Selection pane to set the order in which the screen readers read the slide contents. When the screen reader reads this slide, it reads the objects in the order they are listed in the Selection pane.
-
On the Home tab, in the Drawing group, select Arrange.
-
In the Arrange menu, select Selection Pane.
-
In the Selection pane, to change the reading order, do one of the following:
-
Drag and drop items to the new location.
-
Select the item and then select the Up arrow button (Bring Forward) or Down arrow button (Send Backward).
-
Use built-in slide designs for inclusive reading order
PowerPoint has built-in slide designs that contain placeholders for text, videos, pictures, and more. They also contain all the formatting, such as theme colors, fonts, and effects. To make sure that your slides are accessible, the built-in layouts are designed so that the reading order is the same for people who see and people who use technology such as screen readers.
-
On the View tab, click Normal.
-
In the Thumbnail pane, locate the place where you want to add the new slide. Right-click, and select New Slide. Click the new slide to select it.
-
On the Design tab, expand the Themes gallery, and select the slide layout that you want. PowerPoint automatically applies this layout to the new slide.
-
Go to the new slide, and add the title and content that you want.
Use captions, subtitles, and alternative audio tracks in videos
PowerPoint supports the playback of video with multiple audio tracks. It also supports closed captions and subtitles that are embedded in video files.
Currently, only PowerPoint for Windows supports insertion and playback of closed captions or subtitles that are stored in files separate from the video. For all other editions of PowerPoint (such as PowerPoint for macOS or the mobile editions), closed captions or subtitles must be encoded into the video before they are inserted into PowerPoint.
Supported video formats for captions and subtitles vary depending on the operating system that you're using. Each operating system has settings to adjust how the closed captions or subtitles are displayed.
Closed captions, subtitles, and alternate audio tracks are not preserved when you use the Compress Media or Optimize Media Compatibility features. Also, when turning your presentation into a video, closed captions, subtitles, or alternate audio tracks in the embedded videos are not included in the video that is saved.
When you use the Save Media as command on a selected video, closed captions, subtitles, and multiple audio tracks embedded in the video are preserved in the video file that is saved.
To make your PowerPoint presentations with videos accessible, ensure the following:
-
Videos include an audio track with video descriptions, if needed, for users that are blind or visually impaired.
-
Videos that include dialogue also include closed captions, in-band closed captions, open captions, or subtitles in a supported format for users that are deaf or hard of hearing.
See also
Rules for the Accessibility Checker
Everything you need to know to write effective alt text
Make your Word documents accessible to people with disabilities
Make your Excel documents accessible to people with disabilities
Make your Outlook email accessible to people with disabilities
Mac: Best practices for making PowerPoint presentations accessible
The following table includes key best practices for creating PowerPoint presentations that are accessible to people with disabilities.
| What to fix | How to find it | Why fix it | How to fix it |
|---|---|---|---|
| Include alternative text with all visuals. Visual content includes pictures, SmartArt graphics, shapes, groups, charts, embedded objects, ink, and videos. | To find missing alternative text, use the Accessibility Checker. | Alternative text helps people who can’t see the screen to understand what’s important in images and other visuals. Avoid using text in images as the sole method of conveying important information. If you must use an image with text in it, repeat that text in the presentation. In the alternative text, briefly describe the image and mention the existence of the text and its intent. | Add alt text to visuals in Microsoft 365 |
| Make sure slide contents can be read in the order that you intend. | Use the Accessibility Checker to find slides that have possible problems with reading order. | When someone who can see reads a slide, they usually read things, such as text or a picture, in the order the elements appear on the slide. In contrast, a screen reader reads the elements of a slide in the order they were added to the slide, which might be very different from the order in which things appear. To make sure everyone reads the contents in the order you intend, it's important to check the reading order. | |
| When creating a new slide, use the built-in slide designs. | PowerPoint contains built-in slide layouts that you can apply to any slide. When you use them with a new slide, these layouts automatically make sure that the reading order works for everyone. | ||
| Add meaningful hyperlink text and ScreenTips. | To determine whether hyperlink text makes sense as standalone information and whether it gives readers accurate information about the destination target, visually scan the slides in your presentation. | People who use screen readers sometimes scan a list of links. Links should convey clear and accurate information about the destination. For example, instead of linking to the text Click here, include the full title of the destination page. You can even use the URL of the page if it's short and descriptive, for example, www.microsoft.com. Tip: You can also add ScreenTips that appear when your cursor hovers over text or images that include a hyperlink. | |
| Ensure that color is not the only means of conveying information. | To find instances of color-coding, visually scan the slides in your presentation. | People who are blind, have low vision, or are colorblind might miss out on the meaning conveyed by particular colors. For example, add an underline to color-coded hyperlink text so that people who are colorblind know that the text is linked even if they can’t see the color. For headings, consider adding bold or using a larger font. | |
| Use sufficient contrast for text and background colors. | To find insufficient color contrast, use the Accessibility Checker. You can also look for text in your spreadsheet that’s hard to read or to distinguish from the background. | Use strong contrast between text and background, so people with low vision can see and use the content. Use dark text on a white or off-white background, or reverse it and use white text on a dark background. White and black schemes also make it easier for people who are colorblind to distinguish text and shapes. | |
| Give every slide a unique title. | To find slides that do not have titles, use the Accessibility Checker. | People who are blind, have low vision, or a reading disability rely on slide titles to navigate. For example, by skimming or using a screen reader, they can quickly scan through a list of slide titles and go right to the slide they want. | |
| Use a simple table structure, and specify column header information. | To ensure that tables don't contain split cells, merged cells, or nested tables, use the Accessibility Checker. | Screen readers keep track of their location in a table by counting table cells. If a table is nested within another table or if a cell is merged or split, the screen reader loses count and can’t provide helpful information about the table after that point. Screen readers also use header information to identify rows and columns. | |
| Use a larger font size (18pt or larger), sans serif fonts, and sufficient white space. | To find potential issues related to fonts or white space, review your slides for areas that look crowded or illegible. | People who have dyslexia describe seeing text “swim together” on a page (the compressing of one line of text into the line below). They often see text merge or distort. For people who have dyslexia or have low vision, reduce the reading load. For example, they may benefit from familiar sans serif fonts, such as Arial or Calibri. Avoid using all capital letters and excessive italics or underlines. Include ample white space between sentences and paragraphs. | |
| Make videos accessible to visually impaired and hearing-impaired users. | Subtitles typically contain a transcription (or translation) of the dialogue. Closed captions typically also describe audio cues such as music or sound effects that occur off-screen. Video description means audio-narrated descriptions of a video's key visual elements. These descriptions are inserted into natural pauses in the program's dialogue. Video description makes video more accessible to individuals who are blind or visually impaired. | Use captions, subtitles, and alternative audio tracks in videos |
Add alt text to visuals in Microsoft 365
The following procedures describe how to add alt text to visuals in your PowerPoint presentations in Microsoft 365:
Notes:
-
For audio and video content, in addition to alt text, include closed captioning for people who are deaf or have limited hearing.
-
To enable right-click on your Mac, make sure that the Secondary click option is selected in System Preferences.
Tip: To write a good alt text, make sure to convey the content and the purpose of the image in a concise and unambiguous manner. The alt text shouldn’t be longer than a short sentence or two—most of the time a few thoughtfully selected words will do. Do not repeat the surrounding textual content as alt text or use phrases referring to images, such as, "a graphic of" or "an image of."
Add alt text to images
PowerPoint does not automatically generate alt texts for images. If you want to add an image that is an icon, screenshot, or other image that is not a photograph, you need to add the alt texts manually.
-
Do one of the following:
-
Right-click an image. Select Edit Alt Text....
-
Select an image. Select Picture Format > Alt Text.

The Alt Text pane opens on the right side of the slide.
-
-
Type 1-2 sentences to describe the image and its context to someone who cannot see it.
Tip: To spell check and correct a word you typed, just right-click the word and select from the suggested alternatives.
Add alt text to shapes
-
Do one of the following:
-
Right-click a shape. Select Edit Alt Text....
Tip: You have to right-click somewhere inside the frame that surrounds the entire shape, not inside one of its parts.
-
Select a shape. Select Shape Format > Alt Text.

The Alt Text pane opens on the right side of the slide.
-
-
Type 1-2 sentences to describe the shape and its context to someone who cannot see it.
Tip: To spell check and correct a word you typed, just right-click the word and select from the suggested alternatives.
Add alt text to SmartArt graphics
-
Do one of the following:
-
Right-click a SmartArt graphic. Select Edit Alt Text....
Tip: You have to right-click somewhere inside the frame that surrounds the entire SmartArt graphic, not inside one of its parts.
-
Select a SmartArt graphic. Select Format > Alt Text.

The Alt Text pane opens on the right side of the slide.
-
-
Type 1-2 sentences to describe the SmartArt graphic and its context to someone who cannot see it.
Tip: To spell check and correct a word you typed, just right-click the word and select from the suggested alternatives.
Add alt text to charts
-
Right-click a chart.
Tip: You have to right-click somewhere inside the frame that surrounds the entire chart, not inside one of its parts.
-
Select Edit Alt Text.... The Alt Text pane opens on the right side of the slide.
-
Type 1-2 sentences to describe the chart and its context to someone who cannot see it.
Tip: To spell check and correct a word you typed, just right-click the word and select from the suggested alternatives.
Make visuals decorative
If your presentation has visuals that are purely decorative, you can mark them as such without needing to write any alt text. When a screen reader finds such an image, it simply announces they are decorative, so the user knows they are not missing any information.
-
To open the Alt Text pane, do one of the following:
-
Right-click a visual. Select Edit Alt Text....
-
Select a visual. Select the visual's Format tab > Alt Text.
-
-
Select the Mark as decorative check box. The text entry field becomes grayed out.
Add alt text to visuals in Office 2019
The following procedures describe how to add alt text to visuals in your PowerPoint presentations in Office 2019:
Notes:
-
For audio and video content, in addition to alt text, include closed captioning for people who are deaf or have limited hearing.
-
To enable right-click on your Mac, make sure that the Secondary click option is selected in System Preferences.
Tip: To write a good alt text, make sure to convey the content and the purpose of the image in a concise and unambiguous manner. The alt text shouldn’t be longer than a short sentence or two—most of the time a few thoughtfully selected words will do. Do not repeat the surrounding textual content as alt text or use phrases referring to images, such as, "a graphic of" or "an image of."
Add alt text to images
To make your presentations accessible to wider audiences, add alt texts to the images in your slides. PowerPoint does not automatically generate alt texts.
-
Do one of the following:
-
Right-click an image. Select Edit Alt Text....
-
Select an image. Select Picture Format > Alt Text.

The Alt Text pane opens on the right side of the slide.
-
-
Type 1-2 sentences to describe the image and its context to someone who cannot see it.
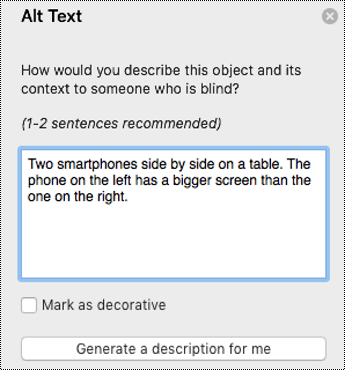
Tip: You can also select Generate a description for me to have Microsoft's cloud-powered intelligent services create a description for you. This takes a moment, after which you see the result in the text entry field. Remember to delete any comments PowerPoint added there, for example, "Description generated with high confidence."
Tip: To spell check and correct a word you typed, just right-click the word and select from the suggested alternatives.
Add alt text to shapes
-
Do one of the following:
-
Right-click a shape. Select Edit Alt Text....
Tip: You have to right-click somewhere inside the frame that surrounds the entire shape, not inside one of its parts.
-
Select a shape. Select Shape Format > Alt Text.

The Alt Text pane opens on the right side of the slide.
-
-
Type 1-2 sentences to describe the shape and its context to someone who cannot see it.
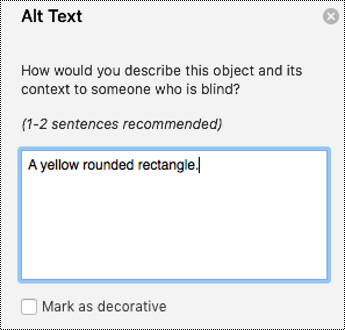
Tip: To spell check and correct a word you typed, just right-click the word and select from the suggested alternatives.
Add alt text to SmartArt graphics
-
Do one of the following:
-
Right-click a SmartArt graphic. Select Edit Alt Text....
Tip: You have to right-click somewhere inside the frame that surrounds the entire SmartArt graphic, not inside one of its parts.
-
Select a SmartArt graphic. Select Format > Alt Text.

The Alt Text pane opens on the right side of the slide.
-
-
Type 1-2 sentences to describe the SmartArt graphic and its context to someone who cannot see it.
Tip: To spell check and correct a word you typed, just right-click the word and select from the suggested alternatives.
Add alt text to charts
-
Right-click a chart.
Tip: You have to right-click somewhere inside the frame that surrounds the entire chart, not inside one of its parts.
-
Select Edit Alt Text.... The Alt Text pane opens on the right side of the slide.
-
Type 1-2 sentences to describe the chart and its context to someone who cannot see it.
Tip: To spell check and correct a word you typed, just right-click the word and select from the suggested alternatives.
Make visuals decorative
If your presentation has visuals that are purely decorative, you can mark them as such without needing to write any alt text. When a screen reader finds such an image, it simply announces they are decorative, so the user knows they are not missing any information.
-
To open the Alt Text pane, do one of the following:
-
Right-click a visual. Select Edit Alt Text....
-
Select a visual. Select the visual's Format tab > Alt Text.
-
-
Select the Mark as decorative check box. The text entry field becomes grayed out.
Add alt text to visuals in Office 2016
The following procedures describe how to add alt text to visuals in your PowerPoint presentations in Office 2016:
Note: For audio and video content, in addition to alt text, include closed captioning for people who are deaf or have limited hearing.
Add alt text to images
Add alt text to images, such as pictures and screenshots, so that screen readers can read the text to describe the image to users who can’t see the image.
-
Right-click an image.
-
Select Format Picture.
-
In the Format Picture pane, select Size & Properties.
-
Select Alt Text and then type a description for the image.
Tip: Include the most important information in the first line, and be as concise as possible.
Add alt text to SmartArt graphics
-
Right-click a SmartArt graphic.
-
Select Format SmartArt, and then select Shape Options.
-
In the Format Shape pane, select Size & Properties.
-
Select Alt Text and then type a description for the SmartArt graphic.
Tip: Include the most important information in the first line, and be as concise as possible.
Add alt text to shapes
Use the following procedure to add alt text to shapes, including shapes within a SmartArt graphic.
-
Right-click a shape.
-
Select Format Shape.
-
In the Format Shape pane, select Size & Properties.
-
Select Alt Text and then type a description for the shape.
Tip: Include the most important information in the first line, and be as concise as possible.
Add alt text to charts
-
Right-click a chart.
-
Select Format Chart Area.
-
In the Format Chart Area pane, on the Chart Options tab, select Size & Properties.
-
Select Alt Text and then type a description for the chart.
Tip: Include the most important information in the first line, and be as concise as possible.
Make hyperlinks, text, and tables accessible
The following procedures describe how to make the hyperlinks, text, and tables in your PowerPoint presentations accessible.
Add hyperlink text and ScreenTips
-
Select the text to which you want to add the hyperlink, and then right-click.
-
Select Hyperlink. The text you selected displays in the Text to Display box. This is the hyperlink text.
-
If necessary, change the hyperlink text.
-
In the Address box, enter the destination address for the hyperlink.
-
Select the ScreenTip button and, in the ScreenTip text box, type a ScreenTip.
Tip: If the title on the hyperlink's destination page gives an accurate summary of what’s on the page, use it for the hyperlink text. For example, this hyperlink text matches the title on the destination page: Templates and Themes for Office Online.
-
To apply the changes, select OK > OK.
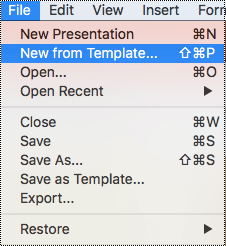
Use an accessible slide design
Use one of the included accessible templates to make sure that your slide design, colors, contrast, and fonts are accessible for all audiences. They are also designed so that screen readers can more easily read the slide content.
-
To find an accessible template, select File > New from Template.
-
In the Search all templates text field, type accessible templates and press Return.
-
In the search results, select a suitable template.
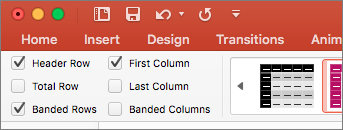
Use table headers
-
Position the cursor anywhere in a table.
-
On the Table Design tab, select the Header Row check box.
-
Type column headers.
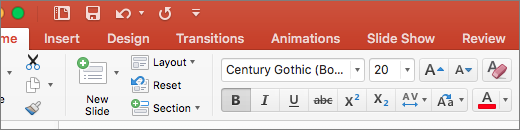
Format text for accessibility
-
Select your text.
-
Select the Home tab.
-
Use the options for font type, size, style, and color to format your text.
Create bulleted lists
-
Position the cursor anywhere in your slide.
-
Select the Home tab.
-
Select the Bullets button.
-
Type the text you want for each bullet item in the list.

Create ordered lists
-
Position the cursor anywhere in your slide.
-
Select the Home tab.
-
Select the Numbering button.
-
Type the text you want for each numbered item in the list.
Make slides accessible
The following procedures describe how to make the slides in your PowerPoint presentations accessible. (See Title a slide for related information.)
Use unique slide titles
-
To restore all placeholders for the selected slide, on the Home tab, select Reset.
-
On the slide, type a unique and descriptive title.
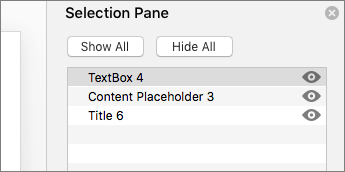
Hide a slide title
Make a title invisible on the slide, but still voiced by screen readers.
-
On the Home tab, select Arrange.
-
In the Arrange menu, select Selection Pane.
-
In the Selection Pane, locate the Title text box, and then click the eye icon next to it.
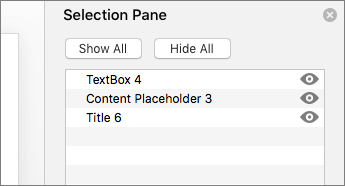
Set the reading order of slide contents
Use the Selection Pane to set the order in which the screen readers read the slide contents. When the screen reader reads this slide, it reads the objects in the order they are listed in the Selection Pane.
-
On the Home tab, select Arrange.
-
In the Arrange menu, select Selection Pane.
-
In the Selection Pane, to change the reading order, drag and drop items to the new location.
Use built-in slide designs for inclusive reading order
PowerPoint has built-in slide designs that contain placeholders for text, videos, pictures, and more. They also contain all the formatting, such as theme colors, fonts, and effects. To make sure that your slides are accessible, the built-in layouts are designed so that the reading order is the same for people who see and people who use technology such as screen readers.
-
On the View tab, click Normal.
-
In the thumbnail pane, locate the place where you want to add the new slide, and then right-click.
-
Select New Slide and then select the inserted slide.
-
On the Design tab, expand the themes gallery, and select the slide layout that you want. PowerPoint automatically applies this layout to the new slide.
-
Go to the new slide, and add the title and content that you want.
Use captions, subtitles, and alternative audio tracks in videos
PowerPoint supports the playback of video with multiple audio tracks. It also supports closed captions and subtitles that are embedded in video files.
Closed captions or subtitles must be encoded into the video before it is inserted into PowerPoint. PowerPoint does not support closed captions or subtitles that are stored in a separate file from the video file.
Supported video formats for captions and subtitles vary depending on the operating system that you're using. Each operating system has settings to adjust how the closed captions or subtitles are displayed.
Closed captions, subtitles, and alternate audio tracks are not preserved when you use the Compress Media or Optimize Media Compatibility features. Also, when turning your presentation into a video, closed captions, subtitles, or alternate audio tracks in the embedded videos are not included in the video that is saved.
When you use the Save Media as command on a selected video, closed captions, subtitles, and multiple audio tracks embedded in the video are preserved in the video file that is saved.
To make your PowerPoint presentations with videos accessible, ensure the following:
-
Videos include an audio track with video descriptions, if needed, for users that are blind or visually impaired.
-
Videos that include dialogue also include closed captions, in-band closed captions, open captions, or subtitles in a supported format for users that are deaf or hard of hearing.
See also
Rules for the Accessibility Checker
Everything you need to know to write effective alt text
Make your Word documents accessible to people with disabilities
Make your Excel documents accessible to people with disabilities
Make your Outlook email accessible to people with disabilities
iOS: Best practices for making PowerPoint presentations accessible
The following table includes key best practices for creating PowerPoint presentations that are accessible to people with disabilities.
| What to fix | Why fix it | How to fix it |
| Include alternative text with all visuals and tables. Visual content includes pictures, shapes, charts, embedded objects, ink, and videos. | Alternative text helps people who can’t see the screen to understand what’s important in images and other visuals. Avoid using text in images as the sole method of conveying important information. If you must use an image with text in it, repeat that text in the presentation. In the alt text, briefly describe the image and mention the existence of the text and its intent. | |
| Ensure that color is not the only means of conveying information. | People who are blind, have low vision, or are colorblind might miss out on the meaning conveyed by particular colors. For example, add an underline to color-coded hyperlink text so that people who are colorblind know that the text is linked even if they can’t see the color. For headings, consider adding bold or using a larger font. | |
| Use sufficient contrast for text and background colors. | The text in your presentations should be readable in High Contrast mode so that everyone, including people with visual disabilities, can see it well. For example, use bright colors or high-contrast color schemes on opposite ends of the color spectrum. White and black schemes make it easier for people who are colorblind to distinguish text and shapes. | |
| Use a simple table structure, and specify column header information. | Screen readers keep track of their location in a table by counting table cells. If a table is nested within another table or if a cell is merged or split, the screen reader loses count and can’t provide helpful information about the table after that point. Screen readers also use header information to identify rows and columns. | |
| Use a larger font size (18pt or larger), sans serif fonts, and sufficient white space. | People who have dyslexia describe seeing text “swim together” on a page (the compressing of one line of text into the line below). They often see text merge or distort. For people who have dyslexia or have low vision, reduce the reading load. For example, they may benefit from familiar sans serif fonts, such as Arial or Calibri. Avoid using all capital letters, and excessive italics or underlines. Include ample white space between sentences and paragraphs. | |
| Make videos accessible to visually impaired and hearing-impaired users | Subtitles typically contain a transcription (or translation) of the dialogue. Closed captions typically also describe audio cues such as music or sound effects that occur off-screen. Video description means audio-narrated descriptions of a video's key visual elements. These descriptions are inserted into natural pauses in the program's dialogue. Video description makes video more accessible to individuals who are blind or visually impaired. | Use captions, subtitles, and alternative audio tracks in videos |
Add alt text to images, tables, and shapes
Add alt text to images, tables, shapes and other visual elements, so that screen readers can read the text to describe the element to users who can’t see it.
-
Select the element, for example, an image.
-
To open the related tab, for example, the Picture tab, tap the Show Ribbon button
 .
. -
Tap Alt Text and type a description for the element. For example, describe the content of the image.
Use an accessible slide design
Use one of the included slide Themes to make sure that your slide design is accessible. Most of the themes are designed for accessible colors, contrast, and fonts. They are also designed so that screen readers can more easily read the slide content.
-
Select a slide.
-
To open the Home tab, tap the Show Ribbon button
 .
. -
Tap Home > Design.
-
Tap Themes and then select the theme you want.

Use table headers
-
Position the cursor anywhere in a table.
-
To open the Table tab, tap the Show Ribbon button
 .
. -
Tap Style Options and then select Header Row.
-
In your table, type the column headings.
Format text for accessibility
-
Select your text.
-
To open the Home tab, tap the Show Ribbon button
 .
. -
On the Home tab, select your text formatting options.
Use captions, subtitles, and alternative audio tracks in videos
PowerPoint supports the playback of video with multiple audio tracks. It also supports closed captions and subtitles that are embedded in video files.
Closed captions or subtitles must be encoded into the video before it is inserted into PowerPoint. PowerPoint does not support closed captions or subtitles that are stored in a separate file from the video file.
Supported video formats for captions and subtitles vary depending on the operating system that you're using. Each operating system has settings to adjust how the closed captions or subtitles are displayed.
Closed captions, subtitles, and alternate audio tracks are not preserved when you use the Compress Media or Optimize Media Compatibility features. Also, when turning your presentation into a video, closed captions, subtitles, or alternate audio tracks in the embedded videos are not included in the video that is saved.
When you use the Save Media as command on a selected video, closed captions, subtitles, and multiple audio tracks embedded in the video are preserved in the video file that is saved.
To make your PowerPoint presentations with videos accessible, ensure the following:
-
Videos include an audio track with video descriptions, if needed, for users that are blind or visually impaired.
-
Videos that include dialogue also include closed captions, in-band closed captions, open captions, or subtitles in a supported format for users that are deaf or hard of hearing.
See also
Rules for the Accessibility Checker
Everything you need to know to write effective alt text
Make your Word documents accessible to people with disabilities
Make your Excel documents accessible to people with disabilities
Make your Outlook email accessible to people with disabilities
Android: Best practices for making PowerPoint presentations accessible
The following table includes key best practices for creating PowerPoint presentations that are accessible to people with disabilities.
| What to fix | Why fix it | How to fix it |
| Include alternative text with all images, shapes, and tables. | Alt text helps people who can’t see the screen to understand what’s important in images and shapes. Avoid using text in images as the sole method of conveying important information. If you must use an image with text in it, repeat that text in the presentation. In alt text, briefly describe the image and mention the existence of the text and its intent. | |
| Ensure that color is not the only means of conveying information. | People who are blind, have low vision, or are colorblind might miss out on the meaning conveyed by particular colors. For example, add an underline to color-coded hyperlink text so that people who are colorblind know that the text is linked even if they can’t see the color. For headings, consider adding bold or using a larger font. | |
| Use sufficient contrast for text and background colors. | The text in your presentations should be readable in High Contrast mode so that everyone, including people with visual disabilities, can see it well. For example, use bright colors or high-contrast color schemes on opposite ends of the color spectrum. White and black schemes make it easier for people who are colorblind to distinguish text and shapes. | |
| Use a simple table structure, and specify column header information. | Screen readers keep track of their location in a table by counting table cells. If a table is nested within another table or if a cell is merged or split, the screen reader loses count and can’t provide helpful information about the table after that point. Screen readers also use header information to identify rows and columns. | |
| Use a larger font size (18pt or larger), sans serif fonts, and sufficient white space. | People who have dyslexia describe seeing text “swim together” on a page (the compressing of one line of text into the line below). They often see text merge or distort. For people who have dyslexia or have low vision, reduce the reading load. For example, they may benefit from familiar sans serif fonts, such as Arial or Calibri. Avoid using all capital letters, and excessive italics or underlines. Include ample white space between sentences and paragraphs. | |
| Make videos accessible to visually impaired and hearing-impaired users | Subtitles typically contain a transcription (or translation) of the dialogue. Closed captions typically also describe audio cues such as music or sound effects that occur off-screen. Video description means audio-narrated descriptions of a video's key visual elements. These descriptions are inserted into natural pauses in the program's dialogue. Video description makes video more accessible to individuals who are blind or visually impaired. | Use captions, subtitles, and alternative audio tracks in videos |
Add alt text to visuals and tables
The following procedures describe how to add alt text to visuals and tables in your PowerPoint presentations.
Note: For audio and video content, in addition to alt text, include closed captioning for people who are deaf or have limited hearing.
Add alt text to images
Add alt text to images such as pictures and screenshots so that screen readers can read the text to describe the image to users who can’t see the image.
-
Select an image.
-
To open the Picture tab, tap the Show Commands button
 .
. -
Scroll down to Alt Text, and then tap it.
-
Type a description for the image.
Add alt text to shapes
-
Select a shape.
-
To open the Shape tab, tap the Show Commands button
 .
. -
Scroll down to Alt Text, and then tap it.
-
Type a description for the shape.

Add alt text to tables
-
Tap anywhere within a table.
-
To open the Table tab, tap the Show Commands button
 .
. -
Scroll down to Alt Text, and then tap it.
-
Type a description for the table.

Mark visuals as decorative
If your visuals are purely decorative and add visual interest but aren't informative, you can mark them as such without needing to write any alt text. Examples of objects that should be marked as decorative are stylistic borders. People using screen readers will hear that these objects are decorative so they know they aren’t missing any important information.
-
To open the Alt Text pane, select an image.
-
To open the formatting menu for the visual, tap the Show Commands button
 .
. -
Scroll down to Alt Text, and then tap it.
-
Tap the Decorative check box. The text entry field becomes grayed out.
Use an accessible slide design
Use one of the included slide Themes to make sure that your slide design is accessible. Most of the themes are designed for accessible colors, contrast, and fonts. They are also designed so that screen readers can more easily read the slide content.
-
Select a slide.
-
To open the Home tab, tap the Show Commands button
 .
. -
Tap Home > Design.
-
Tap Themes, and then select the theme you want.
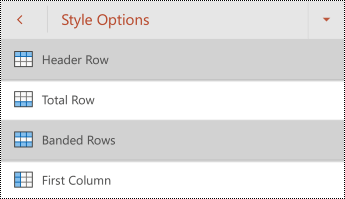
Use table headers
-
Position the cursor anywhere in a table.
-
To open the Table tab, tap the Show Commands button
 .
. -
Tap Style Options, and then select Header Row.
Tip: When the option is already selected, it’s grayed out.
-
In your table, type the column headings.
Format text for accessibility
-
Select your text.
-
To open the Home tab, tap the Show Commands button
 .
. -
On the Home tab, select your text formatting options.
Use captions, subtitles, and alternative audio tracks in videos
PowerPoint supports the playback of video with multiple audio tracks. It also supports closed captions and subtitles that are embedded in video files.
Closed captions or subtitles must be encoded into the video before it is inserted into PowerPoint. PowerPoint does not support closed captions or subtitles that are stored in a separate file from the video file.
Supported video formats for captions and subtitles vary depending on the operating system that you're using. Each operating system has settings you can use to adjust how the closed captions or subtitles are displayed.
Closed captions, subtitles, and alternate audio tracks are not preserved when you use the Compress Media or Optimize Media Compatibility features. Also, when turning your presentation into a video, closed captions, subtitles, or alternate audio tracks in the embedded videos are not included in the video that is saved.
When you use the Save Media as command on a selected video, closed captions, subtitles, and multiple audio tracks embedded in the video are preserved in the video file that is saved.
To make your PowerPoint presentations accessible, ensure the following:
-
Videos include an audio track with video descriptions, if needed, for users that are blind or visually impaired.
-
Videos that include dialogue also include closed captions, in-band closed captions, open captions, or subtitles in a supported format for users that are deaf or hard of hearing.
See also
Rules for the Accessibility Checker
Everything you need to know to write effective alt text
Make your Word documents accessible to people with disabilities
Make your Excel documents accessible to people with disabilities
Make your Outlook email accessible to people with disabilities
Windows 10 app: Best practices for making PowerPoint presentations accessible
The following table includes key best practices for creating PowerPoint presentations that are accessible to people with disabilities.
| What to fix | Why fix it | How to fix it |
| Include alternative text with all images, shapes, and tables. | Alt text helps people who can’t see the screen to understand what’s important in images and shapes. Avoid using text in images as the sole method of conveying important information. If you must use an image with text in it, repeat that text in the presentation. In alt text, briefly describe the image and mention the existence of the text and its intent. | |
| Ensure that color is not the only means of conveying information. | People who are blind, have low vision, or are colorblind might miss out on the meaning conveyed by particular colors. For example, add an underline to color-coded hyperlink text so that people who are colorblind know that the text is linked even if they can’t see the color. For headings, consider adding bold or using a larger font. | |
| Use sufficient contrast for text and background colors. | The text in your presentations should be readable in High Contrast mode so that everyone, including people with visual disabilities, can see it well. For example, use bright colors or high-contrast color schemes on opposite ends of the color spectrum. White and black schemes make it easier for people who are colorblind to distinguish text and shapes. | |
| Use a simple table structure, and specify column header information. | Screen readers keep track of their location in a table by counting table cells. If a table is nested within another table or if a cell is merged or split, the screen reader loses count and can’t provide helpful information about the table after that point. Screen readers also use header information to identify rows and columns. | |
| Use a larger font size (18pt or larger), sans serif fonts, and sufficient white space. | People who have dyslexia describe seeing text “swim together” on a page (the compressing of one line of text into the line below). They often see text merge or distort. For people who have dyslexia or have low vision, reduce the reading load. For example, they may benefit from familiar sans serif fonts, such as Arial or Calibri. Avoid using all capital letters, and excessive italics or underlines. Include ample white space between sentences and paragraphs. | |
| Make videos accessible to visually impaired and hearing-impaired users. | Subtitles typically contain a transcription (or translation) of the dialogue. Closed captions typically also describe audio cues such as music or sound effects that occur off-screen. Video description means audio-narrated descriptions of a video's key visual elements. These descriptions are inserted into natural pauses in the program's dialogue. Video description makes video more accessible to individuals who are blind or visually impaired. | Use captions, subtitles, and alternative audio tracks in videos |
Add alt text to visuals and tables
The following procedures describe how to add alt text to visuals and tables in your PowerPoint presentations.
Note: For audio and video content, in addition to alt text, include closed captioning for people who are deaf or have limited hearing.
Add alt text to images
Add alt text to images such as pictures and screenshots so that screen readers can read the text to describe the image to users who can’t see the image.
-
Select an image.
-
To open the Picture tab, tap the More options button.
-
Scroll down to Alt Text and tap it.
-
Type a description for the image.

Add alt text to shapes
-
Select a shape.
-
To open the Shape tab, tap the More options button.
-
Scroll down to Alt Text and tap it.
-
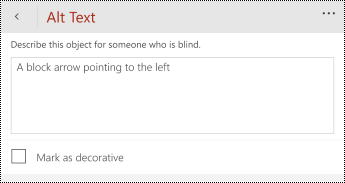
Type a description for the shape.
Add alt text to tables
-
Tap anywhere within a table.
-
To open the Table tab, tap the More options button.
-
Scroll down to Alt Text and tap it.
-
Type a description for the table.

Make visuals decorative
If your presentation has visuals that are purely decorative, you can mark them as such without needing to write any alt text. When a screen reader finds such an image, it simply announces they are decorative, so the user knows they are not missing any information.
-
To open the Alt Text pane, select a visual.
-
Scroll down to Alt Text and tap it.
-
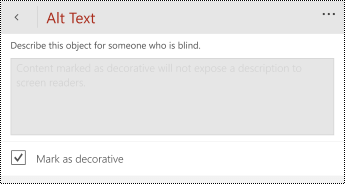
Select the Mark as decorative check box. The text entry field becomes grayed out.
Use an accessible slide design
Use one of the included slide Themes to make sure that your slide design is accessible. Most of the themes are designed for accessible colors, contrast, and fonts. They are also designed so that screen readers can more easily read the slide content.
-
Select a slide.
-
To open the Home tab, tap the More Options button.
-
Tap Home > Design.
-
Tap Themes, and then select the theme you want.
Use table headers
-
Position the cursor anywhere in a table.
-
To open the Table tab, tap the More Options button.
-
Tap Style Options, and then select Header Row.
Tip: When the option is already selected, it’s grayed out.
-
In your table, type the column headings.
Format text for accessibility
-
Select your text.
-
To open the Home tab, tap the More Options button.
-
On the Home tab, select your text formatting options.
Use captions, subtitles, and alternative audio tracks in videos
PowerPoint supports the playback of video with multiple audio tracks. It also supports closed captions and subtitles that are embedded in video files.
Closed captions or subtitles must be encoded into the video before it is inserted into PowerPoint. PowerPoint does not support closed captions or subtitles that are stored in a separate file from the video file.
Supported video formats for captions and subtitles vary depending on the operating system that you're using. Each operating system has settings you can use to adjust how the closed captions or subtitles are displayed.
Closed captions, subtitles, and alternate audio tracks are not preserved when you use the Compress Media or Optimize Media Compatibility features. Also, when turning your presentation into a video, closed captions, subtitles, or alternate audio tracks in the embedded videos are not included in the video that is saved.
When you use the Save Media as command on a selected video, closed captions, subtitles, and multiple audio tracks embedded in the video are preserved in the video file that is saved.
To make your PowerPoint presentations accessible, ensure the following:
-
Videos include an audio track with video descriptions, if needed, for users that are blind or visually impaired.
-
Videos that include dialogue also include closed captions, in-band closed captions, open captions, or subtitles in a supported format for users that are deaf or hard of hearing.
See also
Rules for the Accessibility Checker
Everything you need to know to write effective alt text
Make your Word documents accessible to people with disabilities
Make your Outlook email accessible to people with disabilities
Make your OneNote notebooks accessible to people with disabilities
Office Online: Best practices for making PowerPoint for the web presentations accessible
The following table includes key best practices for creating PowerPoint for the web presentations that are accessible to people with disabilities.
| What to fix | How to find it | Why fix it | How to fix it |
|---|---|---|---|
| Include alternative text with all visuals and tables. Visual content includes pictures, SmartArt graphics, shapes, groups, embedded objects, and videos. | To find missing alternative text, use the Accessibility Checker. | Alternative text helps people who can’t see the screen to understand what’s important in images and other visuals. Avoid using text in images as the sole method of conveying important information. If you must use an image with text in it, repeat that text in the presentation. In the alt text, briefly describe the image and mention the existence of the text and its intent. | Add alt text to SmartArt graphics |
| Add meaningful hyperlink text. | To determine whether hyperlink text makes sense as standalone information and whether it gives readers accurate information about the destination target, visually scan the slides in your presentation. | People who use screen readers sometimes scan a list of links. Links should convey clear and accurate information about the destination. For example, instead of linking to the text Click here, include the full title of the destination page. You can even use the URL of the page if it's short and descriptive, for example, www.microsoft.com. | |
| Ensure that color is not the only means of conveying information. | To find instances of color-coding, visually scan the slides in your presentation. | People who are blind, have low vision, or are colorblind might miss out on the meaning conveyed by particular colors. For example, add an underline to color-coded hyperlink text so that people who are colorblind know that the text is linked even if they can’t see the color. For headings, consider adding bold or using a larger font. Circle or use animation to highlight information, rather than relying on laser pointers or color. Add shapes if color is used to indicate status. For example, add a checkmark symbol if green is used to indicate “pass” and an uppercase X if red indicates “fail”. | |
| Use sufficient contrast for text and background colors. | To find insufficient color contrast, look for slide text that’s hard to read or to distinguish from the background. | The text in your presentations should be readable so that everyone, including people with visual disabilities, can see it well. For example, use bright colors or high-contrast color schemes on opposite ends of the color spectrum. White and black schemes make it easier for people who are colorblind to distinguish text and shapes. Avoid using orange, red, and green in your template and text. Use patterns in graphs, instead of color, to highlight points of interest. | |
| Give every slide a unique title. | Use the Accessibility Checker to find slides that don't have titles. | People who use screen readers and other assistive technology hear slide text, shapes, and content read back in a specific order. That’s why it’s a good practice to use the slide layouts in PowerPoint for the web, which ensure that content is read in a logical order by screen readers. People who are blind, have low vision, or a reading disability rely on slide titles to navigate. For example, by skimming or using a screen reader, they can quickly scan through a list of slide titles and go right to the slide they want. | |
| Use a simple table structure, and specify column header information. | To ensure that tables don't contain split cells, merged cells, or nested tables use the Accessibility Checker. | Screen readers keep track of their location in a table by counting table cells. If a table is nested within another table or if a cell is merged or split, the screen reader loses count and can’t provide helpful information about the table after that point. Screen readers also use header information to identify rows and columns. | |
| Use a larger font size (18pt or larger), sans serif fonts, and sufficient white space. | To find potential issues related to fonts or white space, review your slides for areas that look crowded or illegible. | People who have dyslexia describe seeing text “swim together” on a page (the compressing of one line of text into the line below). They often see text merge or distort. For people who have dyslexia or have low vision, reduce the reading load. For example, they may benefit from familiar sans serif fonts, such as Arial or Calibri. Avoid using all capital letters and excessive italics or underlines. Include ample white space between sentences and paragraphs. |
Add alt text to images and tables
The following procedures describe how to add alt text to images and tables in your PowerPoint for the web presentations.
Note: For audio and video content, in addition to alt text, include closed captioning for people who are deaf or have limited hearing.
Add alt text to images
-
Do one of the following:
-
Right-click an image. Select Edit Alt Text....
-
Select an image. Select Format > Alt Text.
-
-
Select Alt Text, and then type a description for the image.
Add alt text to SmartArt graphics
-
Select a SmartArt graphic.
-
Select Design > Alt Text.
-
Type a description for the SmartArt graphic.
Add alt text to shapes or embedded videos
-
Select a shape or video.
-
Select Format > Alt Text.
-
Type a description for the shape or video.
Add alt text to tables
-
Place the cursor in a cell of the table.
-
Select Layout > Alt Text.
-
Type a description for the table.
Make hyperlinks and tables accessible
The following procedures describe how to make the hyperlinks and tables in your PowerPoint for the web presentations accessible.
Add hyperlink text
-
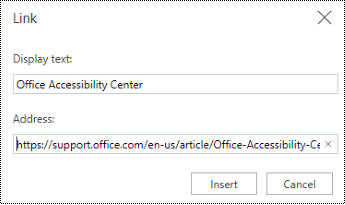
Select the text to which you want to add the hyperlink, right-click, and select Link.
The text you selected displays in the Display text box. This is the hyperlink text.
Tip: If the title on the hyperlink's destination page gives an accurate summary of what’s on the page, use it for the hyperlink text. For example, this hyperlink text matches the title on the destination page: Templates and Themes for Office Online.
-
In the Address box, type or paste the destination URL.
-
Select Insert.
Change the text of a hyperlink
-
Select the text of the hyperlink, right-click, and select Edit Link.
-
In the Display text box, edit the text you want to appear for the hyperlink.
-
Select OK.
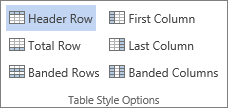
Use table headers
-
Position the cursor anywhere in a table.
-
On Table Tools tab, select Design.
-
Select Header Row, and then type the column headings in the table.
Make slides accessible
The following procedures describe how to make the slides in your PowerPoint for the web presentations accessible.
Use an accessible slide design
Use one of the included accessible themes and templates to make sure that your slide design, colors, contrast, and fonts are accessible for all audiences. They are also designed so that screen readers can more easily read the slide content.
-
In your browser, go to Office.com, sign in to your account, and open PowerPoint for the web.
-
On the Welcome to PowerPoint page, select More themes.
-
On the Select a theme page, scroll down to the bottom of the page, and select Explore all themes.
-
In the Search Office templates text box, type "accessible templates," and press Enter.
-
In the search results, select a suitable template.
-
In the template preview window, select Edit in browser.
Use a logical reading order
If your slides contain objects that aren’t part of a slide template, you need to arrange them in a logical order. Objects are read in the order you added them to a slide, which might not make sense when using a screen reader.
It’s easier to test the reading order in the PowerPoint desktop version because you can rearrange the order of objects in the Selection pane. In PowerPoint for the web, you can cut and paste objects to change their order on a slide.
To test the order of objects on a slide, select the object, and then press the Tab key to switch the focus from object to object.
Format text for accessibility
-
Select your text.
-
Select the Home tab.
-
In the Font group, select your formatting options.
Use unique titles for slides
-
Select a slide without a title.
-
On the Home tab, select Layout.
-
In the Slide Layout dialog, select a slide layout that includes title placeholders, and then select Change Layout. The new layout is applied to the slides.
-
In the title placeholder, type a unique name.
Note: A title doesn’t necessarily have to be visible to be accessible. For example, people who use screen readers hear a slide’s title even if it isn’t visible. In the PowerPoint desktop version, you can use the Selection pane to turn visibility on or off for titles and other objects on a slide.
See also
Improve accessibility with the Accessibility Checker
Rules for the Accessibility Checker
Everything you need to know to write effective alt text
Make your Word documents accessible to people with disabilities
Make your Excel documents accessible to people with disabilities
Make your Outlook email accessible to people with disabilities
Technical support for customers with disabilities
Microsoft wants to provide the best possible experience for all our customers. If you have a disability or questions related to accessibility, please contact the Microsoft Disability Answer Desk for technical assistance. The Disability Answer Desk support team is trained in using many popular assistive technologies and can offer assistance in English, Spanish, French, and American Sign Language. Please go to the Microsoft Disability Answer Desk site to find out the contact details for your region.
If you are a government, commercial, or enterprise user, please contact the enterprise Disability Answer Desk.